Automation in SMEs

Rise in automation is changing the ways of doing business. Similar to the digital and technological revolution, big business houses have been the first to adopt automation across their activities in the form of driverless cars, robot assistants, and delivery drones etc. For example, the Dubai Metro is already driverless, and the UAE is pioneering the Dubai Autonomous Transportation Strategy aiming to make 25 per cent of all trips autonomous by 2030. With progress in automation, the costs of sensors and artificial intelligence are decreasing making automation more economically viable.
All of this has great relevance for the SMEs as they can equally well exploit the benefits from automation. In SMEs automation has potential both in manufacturing, services and business processes. Consulting firm TechSci Research reported that the GCC market for industrial and building automation will reach $10.3 billion in 2023, growing at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 10.7% compared to only $5.6 billion in 2017. Increasingly across the Middle East, automation is becoming more relevant, especially as manufacturers seek to increase productivity and safety whilst the consumer demands higher quality and better value for money.
Industrial automation has been around for some time, but in recent years, business process automation is progressing rapidly. Business automation ensures that the multiple processes in business, that were once scattered, no longer operate in silos. Procurement, sales, operations, and payments are integrated, giving rise to a more clear and real time view of the business.
SMEs- Definition and Global Picture
Small and Medium sized Enterprises (SMEs) are emerging as the backbone of modern economies.
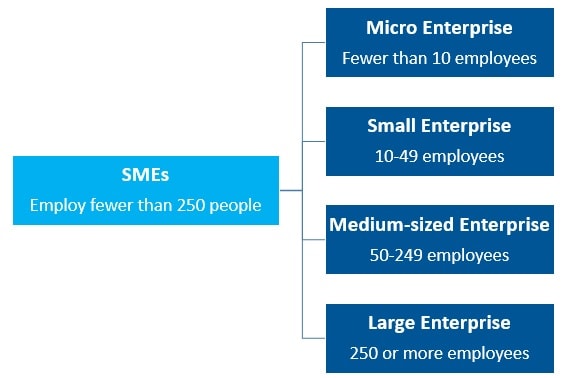
Source: OECD
In terms of contribution to GDP, the role of SMEs is the greatest in Brazil at 61%, China at 60%, and United States at 50 percent and the EU average at 55 percent. Automation is spanning across business models and industries, and is no more limited to the big businesses. Small businesses are leading in automation with 18 percent having already automated parts of their business compared to 15 percent of mid-size firms (smallbusiness.co.uk). Both the developed countries and the Newly Industrialized Economies (NIEs) such as Taiwan, South Korea and Singapore are leading in automation especially in factories. According to a World Economic Forum estimate of 2016, an estimated 1.6 million manufacturing and production jobs will be replaced between 2015 and 2020.
SMEs in the GCC have a key role in contributing towards economic growth and employment creation. According to the 2017 estimates by the Ministry of Economy, SMEs account for 94 per cent of companies operating in UAE, and provide jobs for more than 86 per cent of the private sector workforce. It is reported that a study by MENA Research Partners, a leading research company in the region suggests that GCC’s SME sector presents a potential of $920 billion with 156% growth expected in the next five years, employing 22 million people. Further, GCC region currently accounts for 34% of the MENA SME sector, around $360 billion per year (26% of their GDP).
Share of SME sector, 2018 (% of GDP)
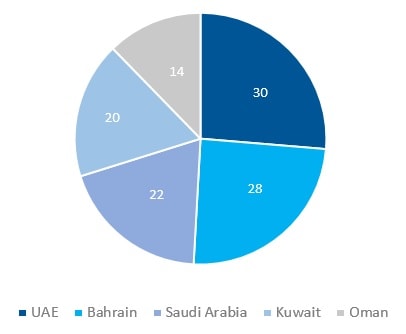 Source: Khaleej Times
Source: Khaleej Times
How is automation used in firms currently?
Dominos developed its Robotic Unit that is an automated delivery system which provides the facility to keep the pizzas hot and the drinks cold. Starship Technologies which partners with Mercedes-Benz Vans use automated bots to deliver food products and other merchandise. Automation is increasingly used in medical field. STAR, a medical service robot, performed an experimental surgery with better accuracy than its human counterparts. Bio-printing creates functioning human organs using a combination of human cells and 3D printing materials. In the real estate sector, automation is employed in activities ranging from supplying contractors, staffing companies, real estate buyers and agents. Customer service has disruption in the form of automated phone service and online digital assistants. Robots are assisting customers in stores to select products and access services.
How can SMEs use automation?
| Technology | Description | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cloud Computing | The cloud reduces the cost of ownership for the SMEs as they do not have to create and maintain separate IT infrastructure. It provides the opportunity to use cutting edge technology without investing heavily. SMEs use cloud for communication, finance and customer management. For example, SMEs can replace their stand-alone, on-site software systems with integrated, cloud-based software solutions that operate on global cloud platforms. For instance, full-service cloud platforms such as Salesforce.com offer access to a wealth of business apps and integrated services. | ||||
| Artificial Intelligence | AI automates and quickly resolves time consuming and repetitive tasks, giving more resources for the SMEs to concentrate on business scaling and building. | ||||
| Big Data | Even small businesses need to find ways to extract knowledge from today’s wealth of Big Data. Automation enables SMEs to process and analyze these huge chunks of data to generate valuable inputs that would enable them to better understand how customers behave, what they need, what to offer them and which business functions to focus on for increased investment. | ||||
| Block-chain | Small businesses that work in industries that serve as intermediaries between two parties – such as lawyers, or real-estate or financial brokers, can use blockchain to eliminate a significant portion of the workload – such as checking and booking transactions, transferring money or paying invoices – handled in these professions today. | ||||
| Mobile Solutions | Smartphones have become the primary device to manage businesses. Mobile solutions in the form of applications are developed for internal communication and organization. For example, in-app payment solutions, enable users to effortlessly make one-click payments and purchase goods using mobile devices or websites. | ||||
| Internet of Things | Enables operational efficiency, increase of productivity, flexibility and agility, IoT can allow SMEs to connect their businesses to the information flowing through an increasing number of smart things. Data originating from sensors built into machines, cars, and consumer goods, will provide valuable consumer data and insights. Therefore, SMEs through IoT, in combination with AI-powered, intelligent backend systems, can create new and superior customer experiences and also better product development. |
Potential Areas where automation can be adopted in SMEs
Automation essentially takes an input, runs it automatically and repeatedly through a set of predetermined commands and returns the results. This makes the automated process scalable and more efficient. Automation ensures that the processes are carried out effectively and the time and resources of the business is spent on networking, building relationships and brainstorming ideas. Some areas which can be directly impacted by automation are as follows:
– Automation in finance: Cloud based solutions provide SMEs the facility to adopt automated procedures such as electronic invoicing, employee self-service management and online procurement. The human intervention and the possibility of errors in manual processing is reduced substantially, leading to streamlining of the process and better financial management. Also an increasing number of new solutions are allowing companies to establish end-to-end payments value chain with their suppliers and customers. These new solutions enable ubiquitous anytime anywhere, immediate and omni-channel payments. They will be fully integrated into the financial accounting systems of the enterprises. All parties, such as ecommerce platforms, banks, fintech companies and their partners, will eventually profit from open API standards which will be used for creating new services and enable seamless, fully-automated processing of payments and financial transactions.
– Automation in HR: the performance and commitment of the employees in SMEs are crucial as they have the first hand responsibility to develop and deliver the product or service. Further, SMEs are characterized by minimum number of employees (250 or less). Therefore, recruiting the right employees and assessing their performance is critical in the SMEs. In case there arises a need for evaluation or further training, an automated process is better capable to identify and address it. The most important benefit of automation in HR is that the managers are able to track the overall performance and monitor features like the KPIs.
– Automation in marketing: Marketing automation software includes tools that enable targeted content and email marketing, SEO, and CRM. It ensures that the content is relevant and the emails are more targeted in nature. It also automatically updates the contact lists, ensuring that communication is effective and timely.
Current-task automation potential for selected occupations
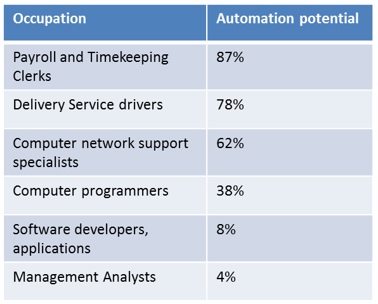
Note: Data is only for US | Source: Brookings
Challenges in automation in SMEs
SMEs have specific challenges around processes that are required to be tackled on a regular basis such as time slicing, scalability and skill sets. It is not necessary and feasible to automate everything in an SME from the first day. Its needs keep evolving as the business develops and activities expand. Therefore, an SME will require a technology that is capable of withstanding regular change and updates as the business grows. A small business features quick transactions and exchanges, therefore there is a need for technology that is fast to operate. They require technology that need the minimum support, time and investment to get restored in case of a breakdown.
Conclusions and Recommendations
The business and operational models of current generation SMEs are inherently different from the traditional businesses. Small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) traverse through several phases in their life cycles—start-up, growth, maturity, and renewal/rebirth or decline—and their business needs vary depending on those phases. Small businesses should adopt intelligent automation to be ahead in the competition. However, there are challenges that need to be overcome for effective implementation of automation:
– Automation requires intelligent and robust programing and networks should be made secure.
– Firms using it need reliable data disciplines.
– SMEs may find it difficult to establish the initial infrastructure, applications, compliance and data security and other critical enablers that ensure speed and quality in automation.
– Automation technologies are simple and intuitive, thereby causing the business teams to automate by themselves. This can lead to proliferation and increase in the future costs of the firm.
To conclude, SMEs will need to grasp the opportunities that technology brings with it and the change it can make to traditional ways of working to stay competitive. The advantage of this is that business administration can become simplified and this will empower entrepreneurs to stay focused on building their businesses and driving growth and leave routine administrative tasks to technology.
