Use of Drones in GCC: Will disrupt logistics, shipping and e-commerce

The use of drones or Unmanned Aerial Vehicle (UAV) for commercial purposes has significantly received attention in the recent years. Adoption of drones is powered mainly by factors such as the increasing need for automation in firms, digitization of internal processes, improving the quality and potential of operational efficiency, and cost optimization requirements.
Apart from adding value to various sectors in the economy with their advanced mechanisms and capabilities, drones are used for short range and light weight applications. One of the most common use of camera installed drones is to capture aerial footage of inaccessible locations. Drones are deployed for studying large sized farmlands, along with monitoring irrigation systems. They provide assistance to farmers in spraying fertilizers, pesticides and water for crops at right times. Further, they are also used for food delivery, 3D mapping and surveillance.
Drones are subjected to continuous technological advancements to make them robust. They are devised to function in challenging conditions and terrains such as dark and extreme climatic conditions.
Drone-powered solutions for commercial applications
Surveying/Mapping: Providing accurate and measurable photogrammetric products to provide better understanding to stakeholders about the area examined
Asset Supervision and Management: Providing crucial information about owned assets and performing stock-taking
Maintenance monitoring: Evaluating the status of work in infrastructure or assets that span across vast or remote areas.
Transport of Goods: Delivering light packages especially used by online retailers
Surveilance: Monitoring behavior activities, operation and other information that would facilitate real time decision making
Source: Strategy&/PwC Analysis
The consumer drone market is expected to generate revenues of more than $9 billion and exceed 15 million units by 2024. It is expected that by 2020, the retail consumer drone market will grow to around US$3.3 billion. The drone industry will have $8 billion to $10 billion worth economic impact worldwide, as well as creating 100,000 jobs globally (Global Market Insights, Inc.).
The market for drones in GCC is projected to reach US$1.5 billion by 2022 (Strategy&). Inspections and surveying will be the most widely used applications along with aerial filming and photography. Drone usage will be incorporated across all stages of projects in the construction sector, in order to achieve a competitive edge and speed up the construction process. Emergency services such as medical deliveries, farming, logistics and cartography applications will be the leading drone use cases in the Middle East.
Drone-powered solutions high-level market size in the GCC (US$ millions, 2022)
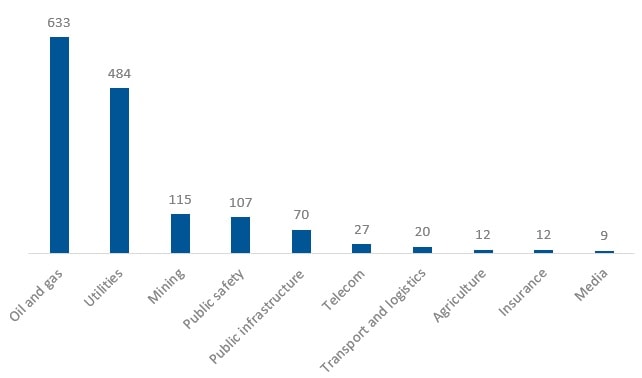 Source: Strategy&
Source: Strategy&
Regionally, UAE government will lead the drone technology development and adoption. In the UAE, various drone applications are piloted especially for traffic monitoring, surveillance, oil spills searches, water and power asset monitoring, litter monitoring, landfill density optimization and police patrols. 70% of the demand for drone technologies will arise from public sector, with an overall increase in the drone flights regionally by at least 150% and the number of drone technology users tripling over the course of 2019 (Zawya). This is expected to increase the demand for Drone-as-a-Service providers, software manufacturers offering data evaluation solutions and hardware vendors in 2019. Drone-mounted sensors are deployed to capture extensive data, leading towards increased digitalization of industrial processes.
Drones were used in mapping the Jebel Jais Flight project, which is the world’s longest zip line measuring at 2.83 kilometers in the mountain region of Jebel Jais. The zip line corridor span from the highest point of approximately 1,600 m to the lower point of 850 m. The deepest of the gully is around 750 m. Drones and structure from motion (SFM) photogrammetry were used to obtain the data from the most inaccessible part of the mountain. In the case of Jabel Jais, drone technology enabled mapping to be delivered in a record time that would otherwise take up to 4-5 times longer if ground surveying was conducted, which was virtually impossible in this project. Drones have significant advantage in terms of precision, convenience and cost in comparison to traditional means like helicopters or satellites. Drones facilitate accurate modelling and mapping, at a cost much lesser than satellites or rental helicopters. As they fly much closer, they are able to obtain resolution of a few centimeters and capture images at unprecedented oblique angles. Drones can fly in a matter of hours, making it possible to react quickly to sudden events. For farmers wanting to assess crop damage or oil companies investigating a drop in a pipeline, the economic benefit of receiving information quickly can overcome the acquisition costs.
Drones are expected to disrupt the logistics, shipping and e-commerce industries. The case of Dubai based Eniverse Technologies to introduce home delivery in the UAE market is an option for many firms to replace the conventional road-based delivery model. These drones will enable the shipment of goods and products weighing 5kg or less to locations across Dubai.
The successful utilization and application of drones depend upon a number of underlying support factors such as sensors, cameras, Global Positioning System (GPS), coordination with sectors like telecom and aviation etc., robust regulatory framework, and investor interest. The safe operation of drones and data collection using them is only a small part of the process. What can be done with the data, how fast it can be processed, and developing the use cases for the data that is collected require assistance from a wide range of technologies such as Artificial Intelligence and 5G.
Although drones have huge commercial value, the technology is prone to multiple cases of misuse including disruption of airspace, use in warfare, threat in high security regions etc. Therefore, drones are banned in various Middle Eastern countries like Algeria, Kuwait, Iran and Syria. GCC countries have strict restrictions with respect to using drones. Oman allows licenses for drones only for commercial purposes whereas in Saudi Arabia, those who own drones or wish to purchase and use it within the country should receive permit from the General Authority for Civil Aviation (GACA).
