التأمين في المملكة العربية السعودية: عروض محتملة غير مستغلة وفرص سريعة النمو
Despite Saudi Arabia’s huge population and the growth witnessed over the past few years, the penetration levels of were lower than UAE and Bahrain. Lower penetration and favourable government policies would serve as strong growth factors.
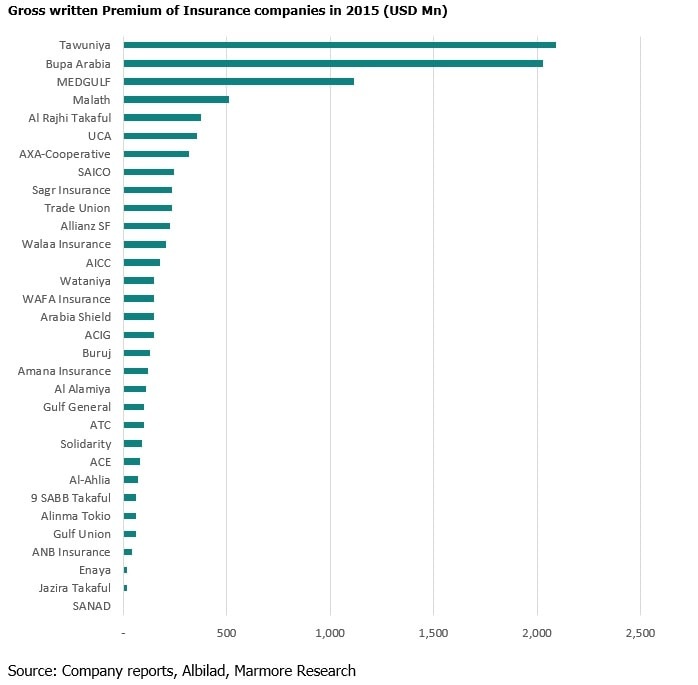
Market Size of Insurance Industry
Saudi Arabia Insurance has a penetration rate of mere 1.5% in 2015 and compared with the developed nations is grossly under insured. With a large population of 32 Mn and strong GDP growth of over 3% there is a lot of potential for the market to grow (IMF Data).
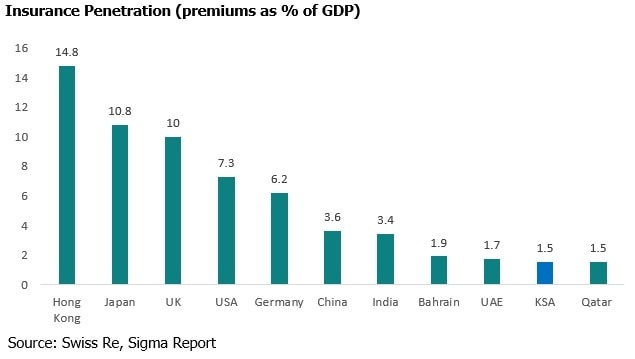
However, it may be limited by Saudi Arabia’s social welfare system, which for the most part is considered generous. Saudi Arabia’s cooperative insurance contributions stand at USD 5.4 billion for 2012 and is projected to reach USD 8.5 billion by the end 2016 making Saudi Arabia the single largest Islamic insurance market in the world.
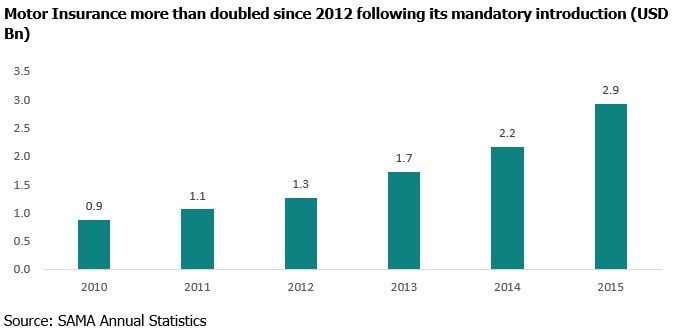
Healthy Uptick in Motor and Health Insurance
Mandatory motor insurance is the main growth driver for the doubling of the premium since 2012. Saudi Arabia is the largest market for auto market for both new and used vehicles and also the largest auto parts markets in the GCC region. Saudi Arabia also imports a large number of automotive products which are then re-exported within the region. Government statistics are hard to come by on the actual number of new vehicle sales however annual sales is estimated to be in the range of 900,000 vehicles during 2015 which is double that of what was sold in 2006.
A total of USD 5.6bn is spent annually on road accidents and there were 526,000 accidents that took place in 2015 resulting in 17 deaths a day. Saudi Arabia is ranked 23rd on the list of countries witnessing the highest death rates in road accidents in the world. It is second among Arab countries in terms of road deaths. The usual causes of accidents include the use of cell phones while driving, ignoring the red light, overtaking from the wrong side and stopping in areas designated for people with special needs. All these factors serve as ideal reasons for increasing acceptance of insurance.
Saudi Arabia was the first nation to provide medical insurance for foreign workers. A new regulation passed in 2006 made it mandatory for employers with more than 500 foreign workers to provide health insurance coverage. This was soon extended to include companies with more than 100 expatriate employees, and in September 2008, was extended, yet again, to companies with more than 50 expatriates. Under article 2 passed in July 2009, health insurance, for the first time, was made compulsory for all Saudis working in the private sector (including those on contract work) for individuals and for family members. Healthcare spending is expected to increase owing to growing and ageing population coupled with increase in lifestyle diseases like obesity and diabetes. Obesity is an endemic in Saudi Arabia with over 70% of adult population classified as obese.
Opportunities for Automation in Underwriting
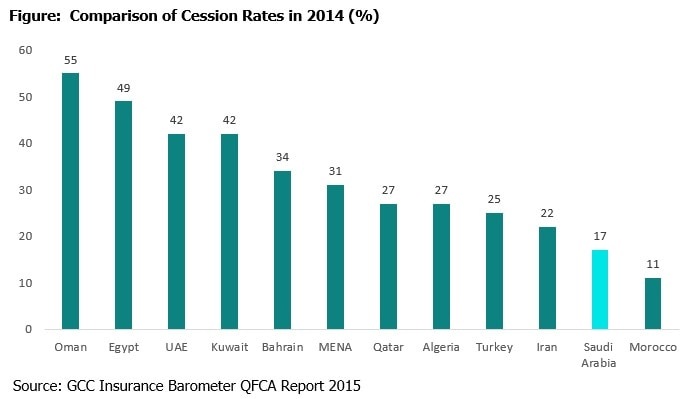
Underwriting process is still carried out manually and underwriters have limited access to information. Automation will improve the efficiency by reducing the errors and rework involved. It can help in classifying and evaluating the risk involved based on the credit history. Due to shortage of efficient underwriting skills the insurers are forced to reinsure considerably. There has been a decline in the cession rates as the health and motor insurance have been made mandatory and maintained by primary insurers. Among the GCC countries, Saudi Arabia has the lowest cession rate but still is high compared to other countries. According to the KSA Reinsurance Regulations, companies must retain not less than 30% of the total written premiums and cannot cede more than 40% of its premiums to reinsurers without SAMA approval. Saudi Arabia had a cession rate of 32% in 2011 which has come down to 17% during 2014. The reduction in cession rates indicates that Saudi Arabia’s insurance have been able to better manage their risks themselves instead of passing them onto re-insurers. While the cession rate has gone down in KSA it is still higher than the global average of 10%.
Possible consolidation among the insurance players
The KSA insurance sector comprises of 35 companies. In addition to that, the KSA insurance sector also comprises of 79 licensed insurance brokers, 83 licensed insurance agencies, one licensed actuarial company, 15 licensed loss assessor companies, 10 licensed claims settlement companies, and eight approved insurance advisors (Standard & Poor’s Ratings Direct).The top three market players dominate the industry with 54% of the total gross premium. Such high level of market concentration and lack of scale for small players could drive consolidation or merger of small players.